a global and intergenerational challenge.
LCA meets EFS

Around 8.5 billion people live on earth today...

Clean drinking water is essential...
and also safe wastewater treatment.

Food must be produced for everyone...
sufficient cultivation + grazing land, irrigation + plant protection form the basis for this.

Energy is needed in all of its manifestions...
electricity, combustibles + fuels ensure comfortable living, communication + mobility.

Urban infrastructure + the agricultural industry compete for land...
because only about a third of the landmass can be used for it. How can it be shared fairly?
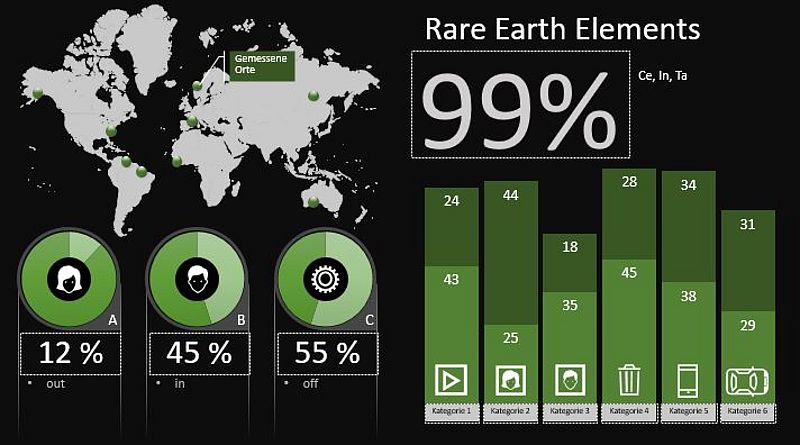
Lack of raw materials and climate protection as a challenge...
new production techniques + recycling conserve resources, reduce emissions + waste.

Consumption can also be sustainable...
change personal behavior.

Education is the beginning...
access to school, training + work are the basis for innovative teamwork.

Science, business, politics + society are jointly challenged...
recognize + understand interrelationships + make them more sustainable.

Understand and apply LCA...
this learning offer is a practical aid + gives examples.
Life Cycle Assessment meets Education for Sustainability
A learning and teaching offer for students of agricultural and environmental sciences, the natural sciences, for engineers and production technicians, for teachers of general schools, for trainees and trainers as well as for the interested public.
This platform is created by an international team of scientists, teachers and didactics and is funded by the German Federal Foundation for the Environment.

WHAT DOES LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT MEAN?
A life cycle analysis, also known as a life cycle assessment (LCA), is a systematic analysis of the environmental impact of products of all kinds along their entire life cycle “from cradle to grave”.
All environmental impacts that occur during production, the use phase and the final disposal of a food or consumer good are described and evaluated. The associated upstream and downstream processes (e.g. the production of raw, auxiliary and operating materials) are also included in an LCA consideration.
Various endpoints can be defined in an LCA. The end point "CO2 footprint" has the highest level of awareness. How it and the other endpoints mentioned are determined, what data flows where, who provides it and how it is meaningfully linked is the subject of this learning platform.
BASIC KNOWLEDGE
To get started with LCA, small fact sheets & learning units are designed to provide condensed basics on the purpose, endpoints (goals), approach, results, and their evaluation.
The materials, link lists, lab scripts, and DATA sets are available for you to download in .pdf, .pptx, or .xlsx file formats. If you prefer to have a Word template, please write to us.(.doc formats are no longer supported by the browser).

FOOD
Selected examples can be used to understand simple to complex LCA from the food sector.
The materials include information for teachers & lecturers, progress plan, worksheets with solutions, DATA sets & lab experiments.
The offerings are modular in nature. The time commitment is at least 1-2 double hours.

CONSUMER GOODS
For the production of everyday items, the necessary materials and energy requirements are outlined and influencing variables are determined.
There is information for teachers & lecturers, course plan, worksheets with solutions, DATA sets & laboratory experiments to choose from. The offerings are modular in nature. The time required is at least 2-3 double hours.


