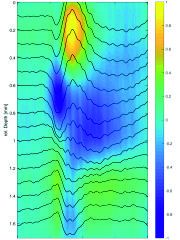
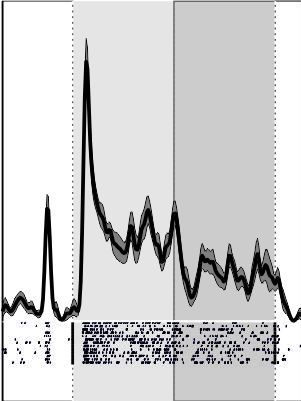
Extracellular Recordings
Neurons communicate via small electric pulses, called action potentials or spikes. In general, a neuron generates a spike (or many of them) when it receives sufficiently strong input at its synapses. Neuronal activity results in changes in the composition of ions in extracellular space and thereby in local variations of the electric field, which can be measured. Such extracellular recordings provide access to the activity of single cells and allow the investigation of communication between individual neurons and groups of neurons with very high spatio-temporal resolution. This is key to understand the neuronal mechanisms subserving cognitive functions, as e.g. attention-dependent improvement of neuronal response selectivity and signal-to noise ratio, coordination of activity in neuronal ensembles, and communication within and across brain areas (e.g. Grothe et al., 2012; Drebitz et al., 2018; Galashan et al., 2013; Schledde et al., 2017).