Welcome to the Lab of Molecular Genetics
Plant Reproduction and Polyspermy
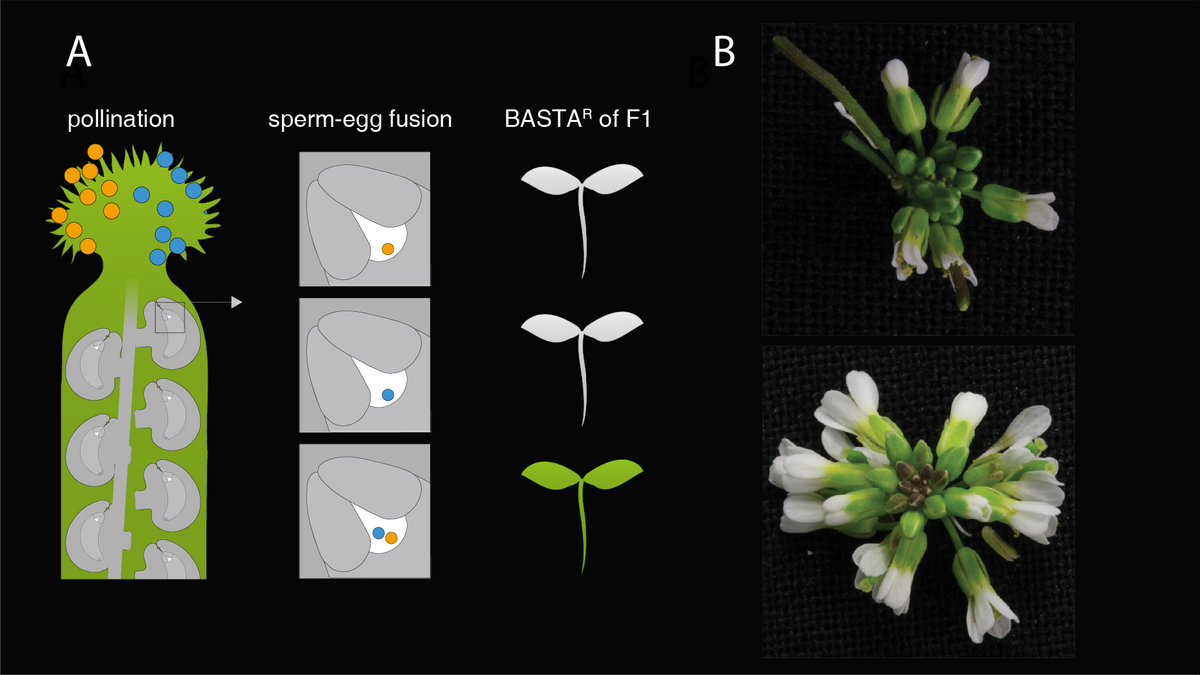
Polyspermy describes the fertilization of an egg by more than one sperm cell. In animals this usually has devastating consequences leading to the death of the newly formed embryo (Nakel et al. 2017).
The discovery that polyspermy in flowering plants is not lethal but generates viable triploid plants is a game changer affecting the field of developmental biology, evolution, and plant breeding (Tekleyohans 2017).
moreMitochondrial Codes and Communication
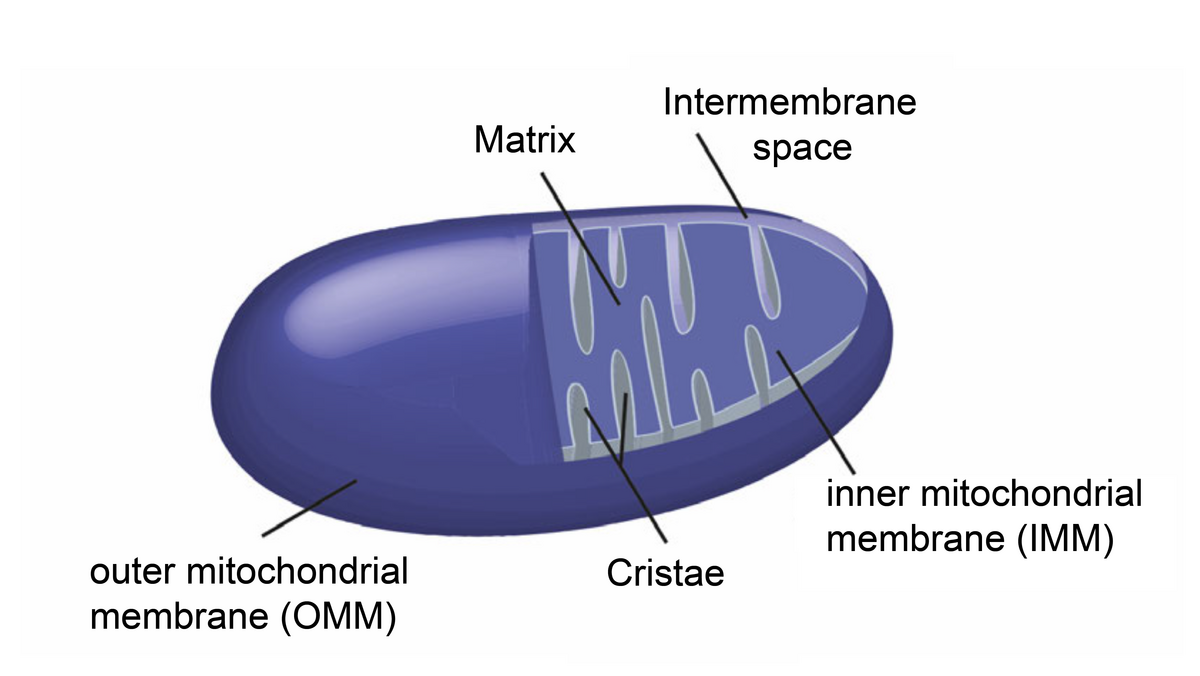
Mitochondria are organelles located inside eukaryotic cells that carry out the essential task of producing energy for the cell.
Apart from producing energy, mitochondria also regulate important cellular processes including signal transduction, redox homeostasis and programmed cell death (1). Or, as Nick Lane once put it “Mitochondria are pivotal in power, sex, and suicide.” (2)
moreReferences
- A. V. Kuznetsov, R. Margreiter, Heterogeneity of mitochondria and mitochondrial function within cells as another level of mitochondrial complexity. Int J Mol Sci 10, 1911-1929 (2009).
- Lane, N. (2005). Power, sex, suicide: Mitochondria and the meaning of life. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
