X-Ray Diffraction
X-ray Diffraction
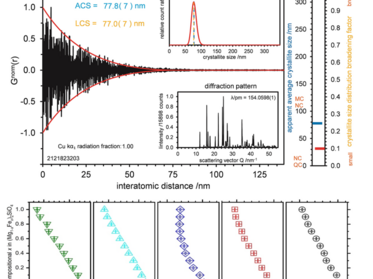
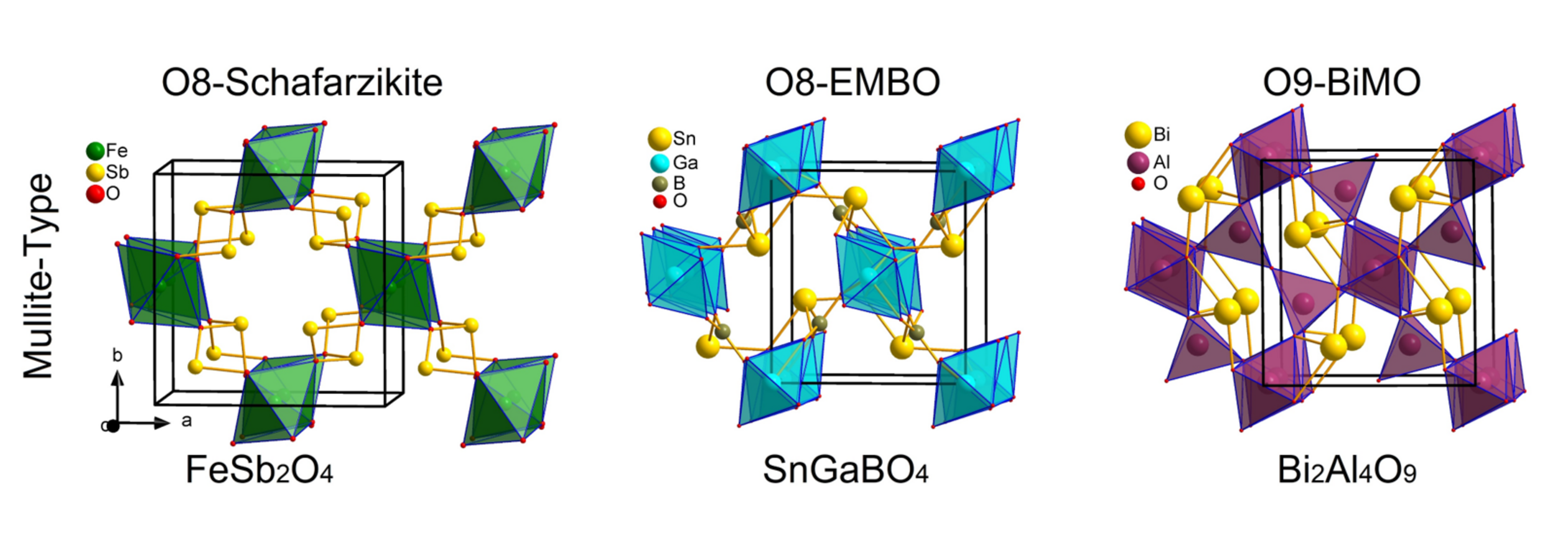
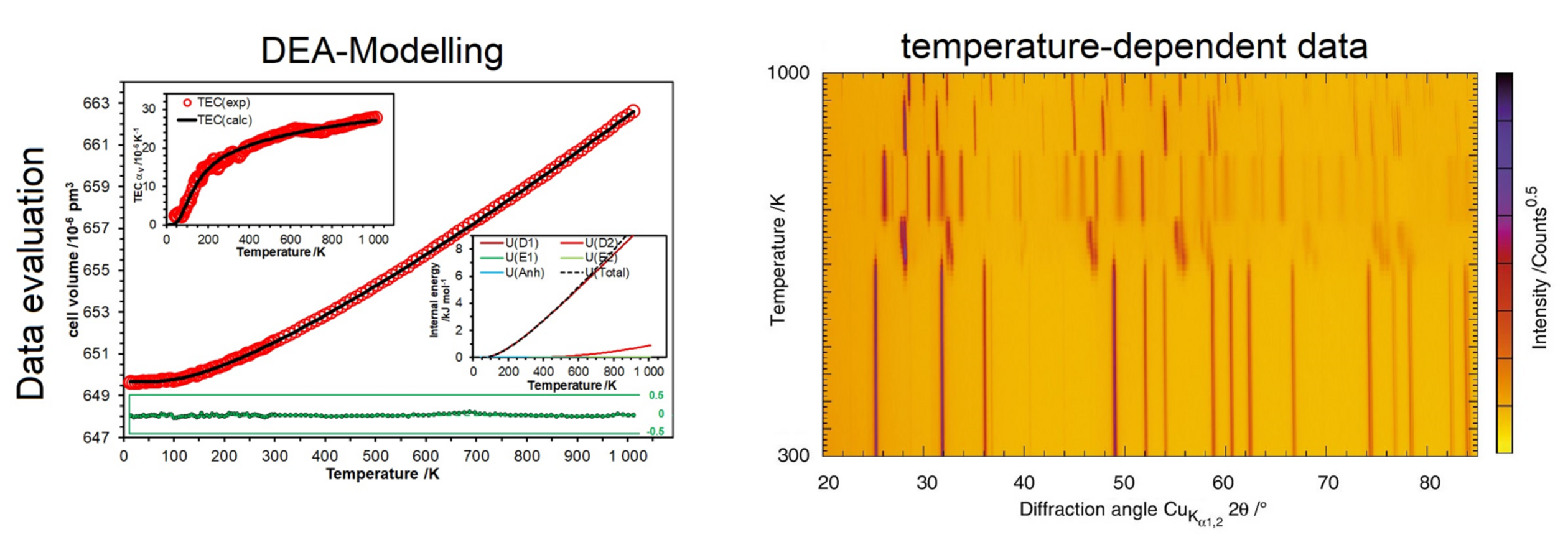
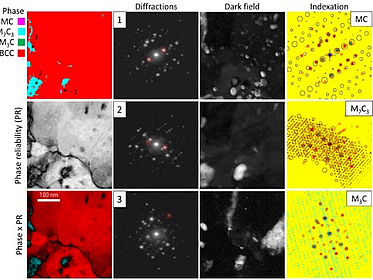
X-rays are scattered by the electronic shells of the atoms. Regular periodic arrangement of the atoms leads to sharp diffraction peaks described by the Bragg-equation, all deviations from the periodicity gives rise to the so-called diffuse scattering. Bragg-scattering can be evaluated by Rietveld-refinements. With adapted measurement techniques the sample’s diffuse scattering can be evaluated as well (Total-Scattering).
What kind of result do I get?
The measurement result is a diffractogram, which is used to determine the phase composition of the sample. In the case of well crystalline samples, Rietveld refinements use the Bragg scattering information to refine an average structure model. Total scattering data can be evaluated using either models based on statistical ensembles of crystallites (genetic-algorithms) or large super-cells of an average structure model in which disorder is included on every atomic position using Reverse-Monte-Carlo methods.
Application Scientist
Dr. Lars Robben
X-ray diffraction and SEM lab head
Radiation protection office @ CKfS
E-mail: lrobbenprotect me ?!uni-bremenprotect me ?!.de
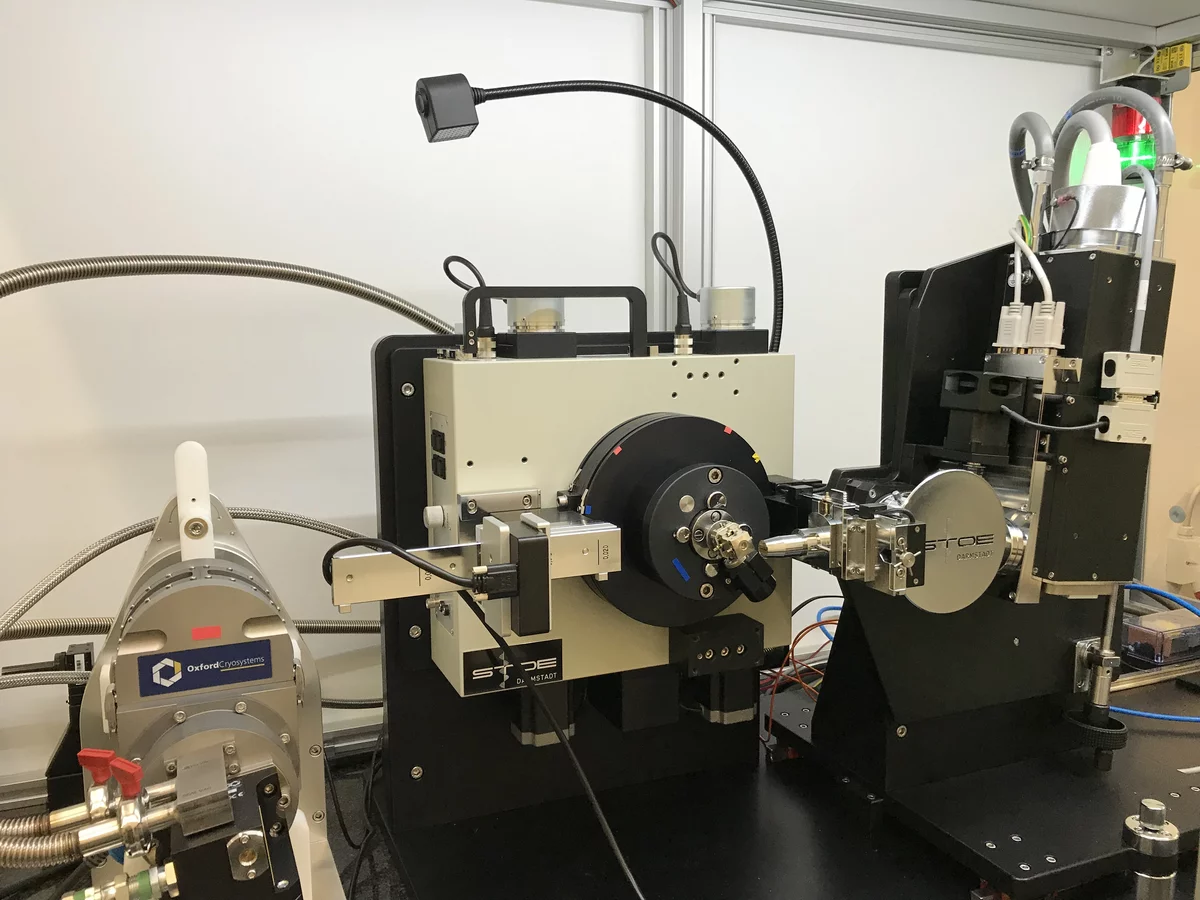
Stoe Stadi MP
Powder X-ray diffractometer
- Transmission and reflection geometry with Mo radiation
- Measurements from 10 K to 1800 K
- Total-scattering pre-measurements for applications at large-scale research facilities
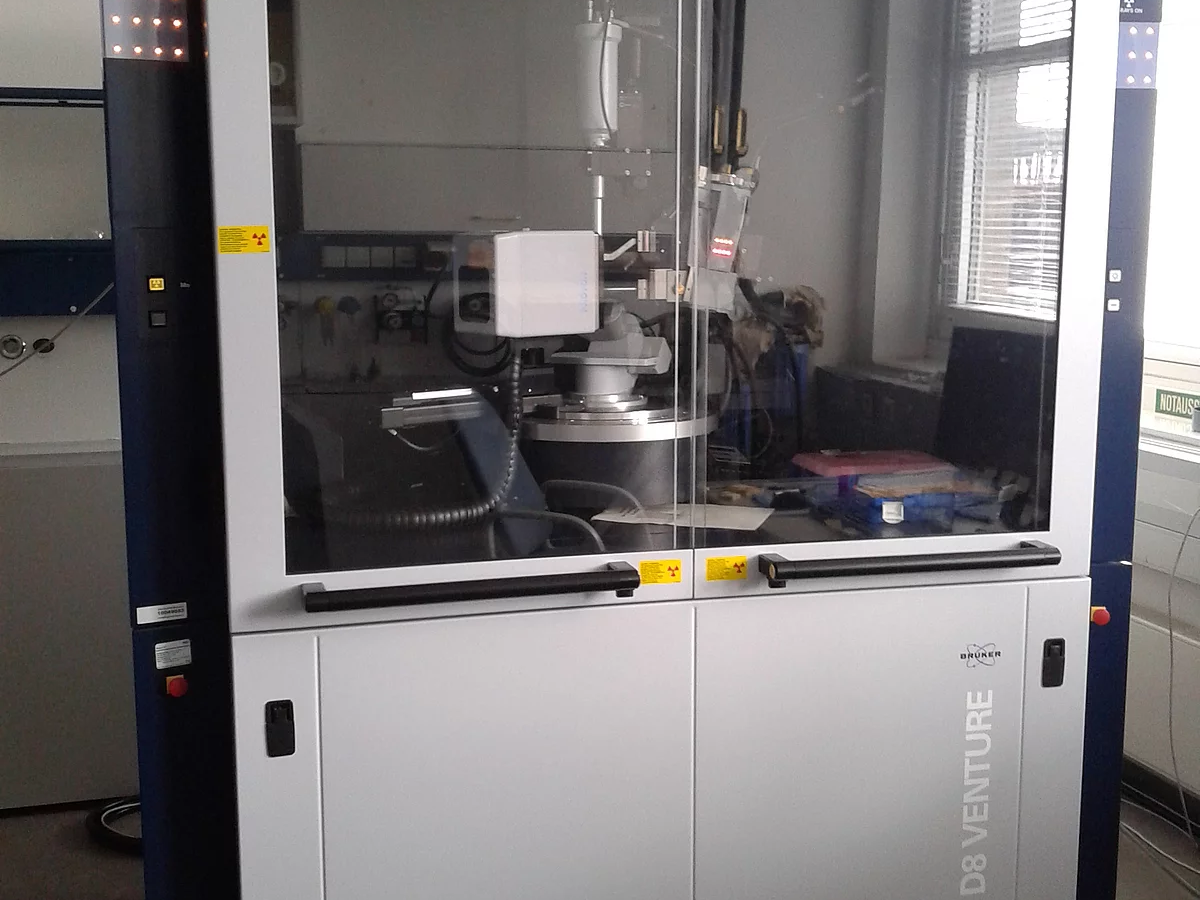

Bruker D8 Venture
4-circle diffractometer
- Monochromatic Mo Kalpha radiation
- 2D detector
- Measurements from 170 K to 1270 K
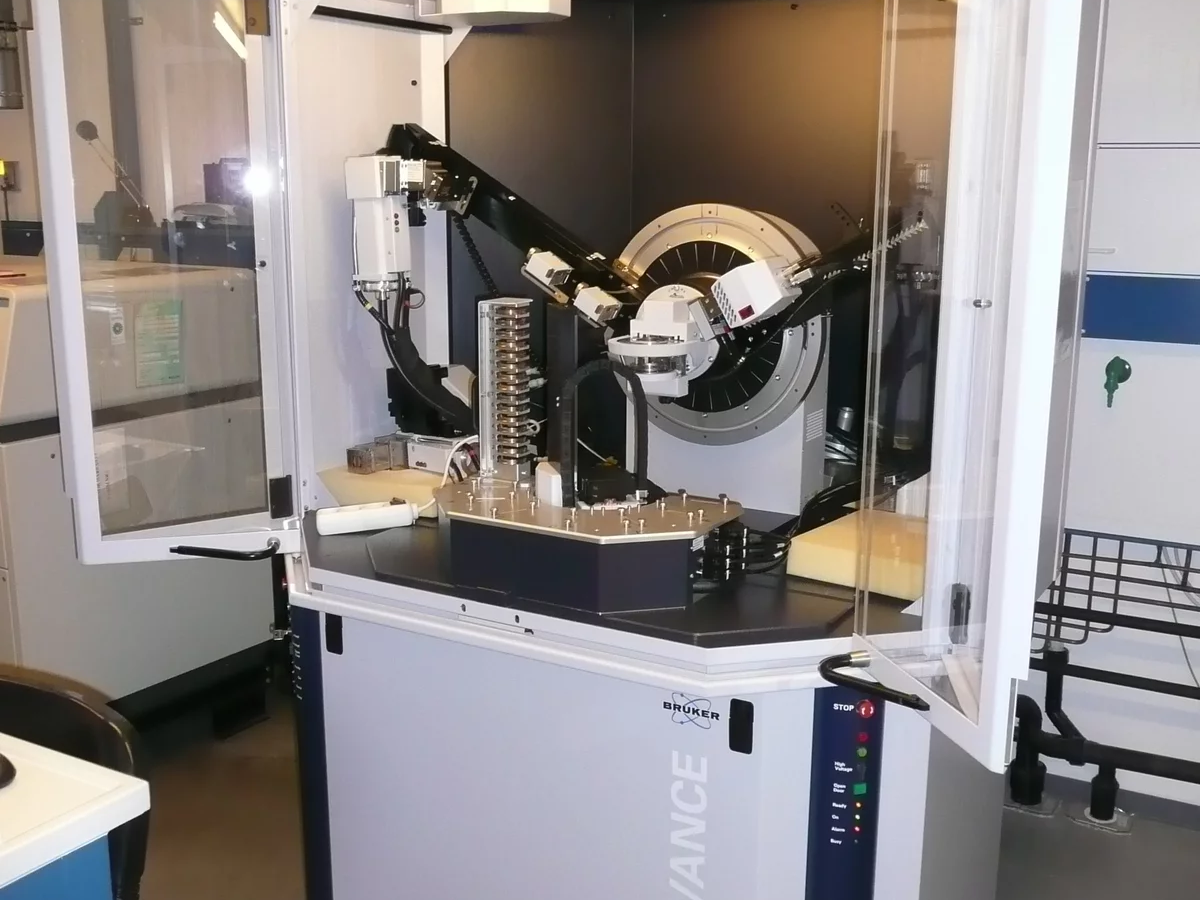

Bruker D8 Advance
Cu and Mo X-ray powder diffractometer
- Bragg-Brentano and transmission geometry
- Measurements from 100 K to 1500 K


Synthesis, structural and spectroscopic characterization of defect-rich forsterite as a representative phase of Martian regolith